Hearing loss is a condition that can develop very gradually, often over the course of many years. Usually the person affected does not realize a hearing loss exists until it begins to cause problems with how they communicate, or their loved ones urge them to seek help. If a hearing loss is detected, early intervention will increase the likelihood of a positive outcome. At Surendra Hearing Clinic we recommend a hearing assessment every one to two years, as part of your regular check-up. An Audiologist will review your previous test results, medical history, noise exposure and conduct a communication assessment to determine if a problem with your hearing is developing. If you are bothered by tinnitus, our tinnitus assessment will provide additional information.
Hearing loss is common and affects all age groups
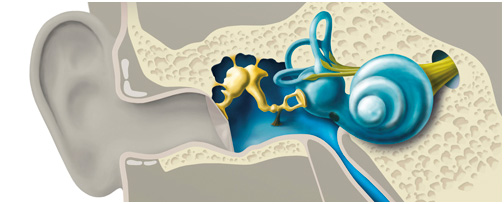
Types of Hearing Loss
1. Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss results from an inner ear disorder. We refer to a sensorineural hearing loss when the hair cells, neural fibers or their connections to the cochlea are damaged or do not function optimally. If part of the inner ear is damaged, the ability to transform mechanical energy into the electrical energy that is sent to the brain is lost or reduced.
Characteristic signs of sensorineural hearing loss
- Difficulties hearing sounds, especially soft sounds
- Difficulties distinguishing and differentiating among sounds, even loud sounds
- Low level sounds are perceived to be far too soft, and high level sounds too loud
- Often accompanied by tinnitus
Causes of sensorineural hearing loss
- Aging
- Noise-induced hearing impairment
- Heredity, congenital
- Illness or medicine (Diabetes, Kidney diseases, Cancers etc.)
Treatment
Hearing loss caused by damage to the inner ear or the nerve paths cannot be treated surgically or medically. Many people with sensorineural loss can, however, benefit from hearing aids.
2. Conductive Hearing Loss
When sound is not conducted optimally through the outer or middle ear, the result is a conductive hearing loss. The specific hearing loss can originate in the outer ear, ear canal, eardrum, ossicles (middle ear bones) or a combination of these. A conductive hearing impairment usually gives rise to a mild to moderate hearing loss. The loss can affect all frequencies relatively uniformly or be especially pronounced in the low-frequency region.
Causes of conductive hearing loss
- Ear wax completely blocking the ear canal
- Inflammation of the middle ear
- Perforation of the eardrum
- Otosclerosis
- Fracture in the chain of ossicles
- Deformity of the outer ear
Treatment
Most conductive hearing losses can be treated medically or surgically, for example when the hearing loss is caused by inflammation of the middle ear. When surgical or medical intervention is not an option, people with conductive hearing loss can often be helped with hearing aids.
3. Mixed Hearing Loss
When a portion of the hearing loss is sensorineural and a portion is conductive, it is referred to as a mixed hearing loss.
